Is Gillette India Limited’s (NSE:GILLETTE) High P/E Ratio A Problem For Investors?

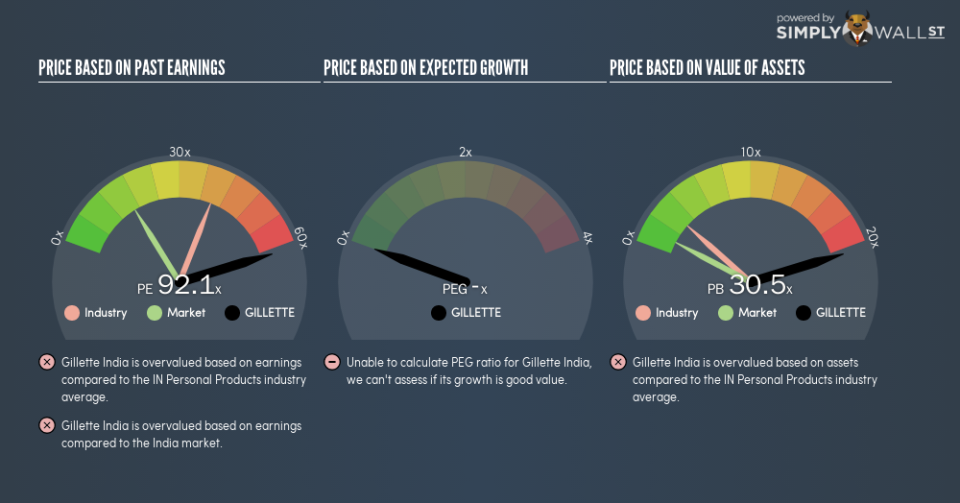
The goal of this article is to teach you how to use price to earnings ratios (P/E ratios). We’ll look at Gillette India Limited’s (NSE:GILLETTE) P/E ratio and reflect on what it tells us about the company’s share price. Based on the last twelve months, Gillette India’s P/E ratio is 92.06. That means that at current prices, buyers pay ₹92.06 for every ₹1 in trailing yearly profits.
See our latest analysis for Gillette India
How Do I Calculate Gillette India’s Price To Earnings Ratio?
The formula for price to earnings is:
Price to Earnings Ratio = Price per Share ÷ Earnings per Share (EPS)
Or for Gillette India:
P/E of 92.06 = ₹6499.95 ÷ ₹70.6 (Based on the trailing twelve months to September 2018.)
Is A High P/E Ratio Good?
A higher P/E ratio means that buyers have to pay a higher price for each ₹1 the company has earned over the last year. That isn’t a good or a bad thing on its own, but a high P/E means that buyers have a higher opinion of the business’s prospects, relative to stocks with a lower P/E.
How Growth Rates Impact P/E Ratios
Probably the most important factor in determining what P/E a company trades on is the earnings growth. When earnings grow, the ‘E’ increases, over time. Therefore, even if you pay a high multiple of earnings now, that multiple will become lower in the future. Then, a lower P/E should attract more buyers, pushing the share price up.
Gillette India’s earnings per share fell by 12% in the last twelve months. But over the longer term (5 years) earnings per share have increased by 30%.
How Does Gillette India’s P/E Ratio Compare To Its Peers?
We can get an indication of market expectations by looking at the P/E ratio. The image below shows that Gillette India has a higher P/E than the average (39.2) P/E for companies in the personal products industry.
Gillette India’s P/E tells us that market participants think the company will perform better than its industry peers, going forward. Clearly the market expects growth, but it isn’t guaranteed. So further research is always essential. I often monitor director buying and selling.
Don’t Forget: The P/E Does Not Account For Debt or Bank Deposits
It’s important to note that the P/E ratio considers the market capitalization, not the enterprise value. That means it doesn’t take debt or cash into account. Hypothetically, a company could reduce its future P/E ratio by spending its cash (or taking on debt) to achieve higher earnings.
Such expenditure might be good or bad, in the long term, but the point here is that the balance sheet is not reflected by this ratio.
How Does Gillette India’s Debt Impact Its P/E Ratio?
The extra options and safety that comes with Gillette India’s ₹2.4b net cash position means that it deserves a higher P/E than it would if it had a lot of net debt.
The Verdict On Gillette India’s P/E Ratio
Gillette India’s P/E is 92.1 which is way above average (16.5) in the IN market. Falling earnings per share is probably keeping traditional value investors away, but the net cash position means the company has time to improve: and the high P/E suggests the market thinks it will.
Investors should be looking to buy stocks that the market is wrong about. As value investor Benjamin Graham famously said, ‘In the short run, the market is a voting machine but in the long run, it is a weighing machine.’ Although we don’t have analyst forecasts, shareholders might want to examine this detailed historical graph of earnings, revenue and cash flow.
You might be able to find a better buy than Gillette India. If you want a selection of possible winners, check out this free list of interesting companies that trade on a P/E below 20 (but have proven they can grow earnings).
To help readers see past the short term volatility of the financial market, we aim to bring you a long-term focused research analysis purely driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis does not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements.
The author is an independent contributor and at the time of publication had no position in the stocks mentioned. For errors that warrant correction please contact the editor at editorial-team@simplywallst.com.