Who Are The Top Investors In Capital Mining Limited (ASX:CMY)?

In this article, I’m going to take a look at Capital Mining Limited’s (ASX:CMY) latest ownership structure, a non-fundamental factor which is important, but remains a less discussed subject among investors. The impact of a company’s ownership structure affects both its short- and long-term performance. Since the same amount of capital coming from an activist institution and a passive mutual fund has different implications on corporate governance, it is a useful exercise to deconstruct XYZ’s shareholder registry. All data provided is as of the most recent financial year end.
See our latest analysis for CMY
Institutional Ownership
Institutional investors typically buy and sell shares in large magnitudes which can significantly sway the share price, especially when there are relatively small amounts of shares available on the market to trade. A low institutional ownership of 2.79% puts CMY on a list of companies that are not likely exposed to spikes in volatility resulting from institutional trading. Low coverage stocks like CMY tend to be favourite picks of legendary investor Peter Lynch, who used to cash in on the rally supported by institutional buying as the stock gained popularity.
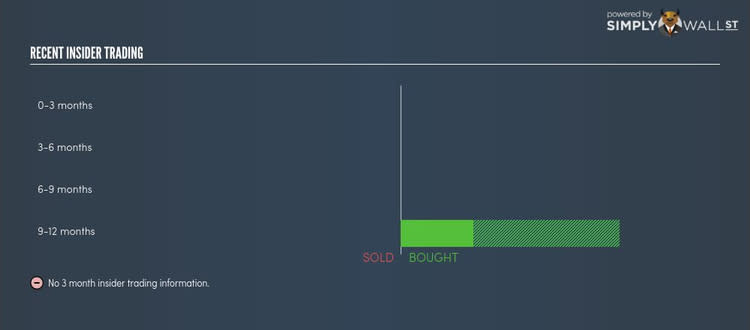
Insider Ownership
Insiders form another group of important ownership types as they manage the company’s operations and decide the best use of capital. Insider ownership has been linked to better alignment between management and shareholders. Although individuals in CMY hold only a 4.82% stake, it’s a good sign for shareholders as the company’s executives and directors have their incentives directly linked to the company’s performance. It would also be interesting to check what insiders have been doing with their shareholding recently. Insider buying can be a positive indicator of future performance, but a selling decision can be simply driven by personal financial requirements.
General Public Ownership
The general public holds a substantial 88.98% stake in CMY, making it a highly popular stock among retail investors. This size of ownership gives retail investors collective power in deciding on major policy decisions such as executive compensation, appointment of directors and acquisitions of businesses. This level of ownership gives retail investors the power to sway key policy decisions such as board composition, executive compensation, and potential acquisitions. This is a positive sign for an investor who wants to be involved in key decision-making of the company.
Private Company Ownership
Another group of owners that a potential investor in CMY should consider are private companies, with a stake of 3.41%. While they invest more often due to strategic interests, an investment can also be driven by capital gains through share price appreciation. However, an ownership of this size may be relatively insignificant, meaning that these shareholders may not have the potential to influence CMY’s business strategy. Thus, investors not need worry too much about the consequences of these holdings.
What this means for you:
Are you a shareholder? With a low level of institutional ownership, investors in CMY need not worry about non-fundamental factors such as ownership structure causing large impact on stock prices. If you’re interested in bolstering your portfolio with new stocks and are looking for ideas, take a look at our free app to see my list of stocks with a strong growth potential.
Are you a potential investor? Ownership structure should not be the only determining factor when you’re building an investment thesis for CMY. Rather, you should be looking at fundamental drivers like the future growth expectations around CMY, which is a key factor that will influence CMY’s share value. Take a look at our most recent infographic report on CMY for a more in-depth analysis of these factors to help you make a more well-informed investment decision.
NB: Figures in this article are calculated using data from the last twelve months, which refer to the 12-month period ending on the last date of the month the financial statement is dated. This may not be consistent with full year annual report figures.
To help readers see pass the short term volatility of the financial market, we aim to bring you a long-term focused research analysis purely driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis does not factor in the latest price sensitive company announcements.
The author is an independent contributor and at the time of publication had no position in the stocks mentioned.